Theoretical study of pulse delay effects in the photoelectron angular distribution of near-threshold EUV+IR two-photon ionization of atoms (2014)
要旨訳:
フェムト秒極紫外(EUV)および近赤外(IR)レーザーパルスの組み合わせによる水素原子および希ガス(He, Ne, Ar)原子の2色2光子イオン化で放出される光電子角度分布(PAD)を理論的に解析した。時間に依存する2次の摂動論を用いて、2光子イオン化プロセスがEUVパルスとIRパルスの遅延にどう依存しているか、および共鳴イオン化経路と非共鳴イオン化経路の競合とどう関係しているかを明らかにした。さらに時間依存シュレーディンガー方程式を解くことで、異方性パラメータ、ならびにPADを形成する部分波間の振幅比と相対位相を解析した。Heをのぞき、これらパラメータはEUVとIRパルスの時間差に著しく依存していることがわかった。この依存性は、光イオン化の共鳴・非共鳴経路の相対的な役割が遅延時間に依存して変化していることによる。H、He、Ne、Arのシミュレーション結果から、パルス遅延効果はS殻からのイオン化よりもP殻からのイオン化で顕著であることがわかった。
Abstract:
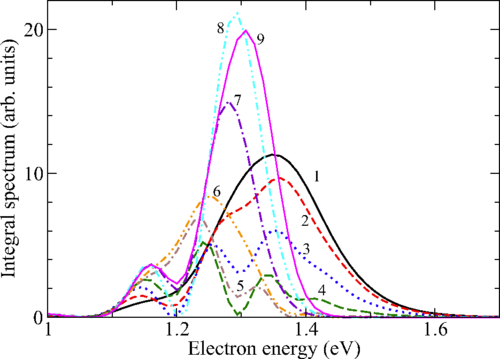
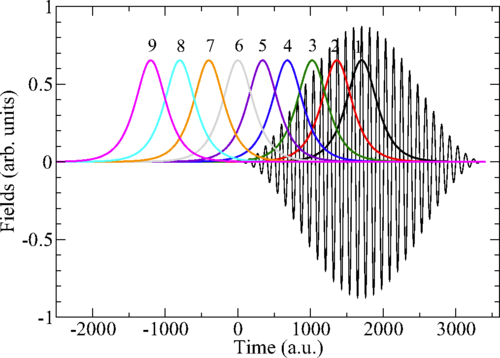
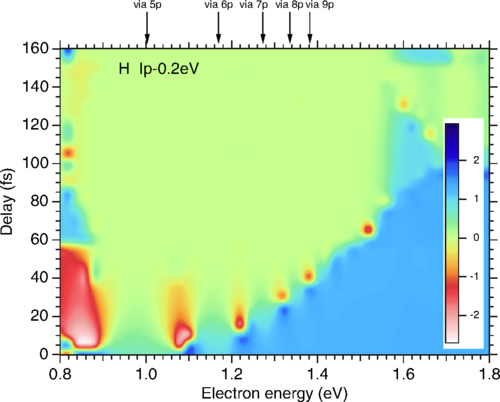
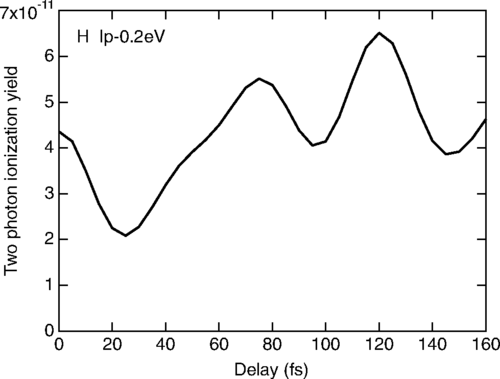
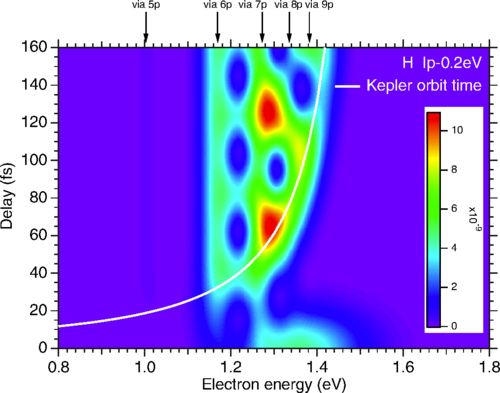
We study theoretically the photoelectron angular distributions (PADs) from two-color two-photon near-threshold ionization of hydrogen and noble gas (He, Ne, and Ar) atoms by a combined action of femtosecond extreme ultraviolet (EUV) and near-infrared (IR) laser pulses. By using second-order time-dependent perturbation theory, we clarify how the two-photon ionization process depends on the EUV-IR pulse delay and how it is connected to the interplay between resonant and nonresonant ionization paths. Furthermore, by solving the time-dependent Schrödinger equation, we calculate the anisotropy parameters β2 and β4 as well as the amplitude ratio and relative phase between partial waves characterizing the PADs. We show that, in general, these parameters notably depend on the time delay between the EUV and IR pulses, except for He. This dependence is related to the varying relative role of resonant and nonresonant paths of photoionization. Our numerical results for H, He, Ne, and Ar show that the pulse-delay effect is more pronounced for p-shell ionization than for s-shell ionization.
Source:
Kenichi L. Ishikawa, A. K. Kazansky, N. M. Kabachnik, and Kiyoshi Ueda, Theoretical study of pulse delay effects in the photoelectron angular distribution of near-threshold EUV+IR two-photon ionization of atoms, Phys. Rev. A 90, 023408 (11 pages) (2014) (http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.90.023408)